Use these practice activities to help you master your Geometry Skills.
Teachers & Parents: It is recommended that students complete and master
each activity before moving on to the next one.
Basic Geometry
Basic Geometry 1
Basic two dimensional shapes and properties.
| Basic Geometry 2
Work with terms like hexagon, square pyramid, rectangular prism.
| Basic Geometry 3
Work with terms like polygon, right angle, faces, sphere, parallel, segment, etc...
| Slideshow with Links
Striking Examples of Geometry in Architecture
|
| | | |
|
Polygon Names 1
Basic polygons.
| Polygon Names 2
Features of polygons.
| Irregular Polygons
Features of irregular polygons.
| The Magic Circle
An Interactive Geometry Overview Lesson (Fun!)
|
| | | |
|
Parallelograms 1
Basic concepts of parallelograms.
| Parallelograms 2
Basic concepts of parallelograms.
| Parallelograms 3
Basic concepts of parallelograms.
| Magic Circle Quiz
A quiz based on parts of the 'Magic Circle' Lesson (above)
|
| | | |
Area
Area Set 1
Use the formula
length x width = Area.
| Area Set 2
Finding area with whole and half units.
| Area Set 3
Finding the area of complex polygons.
| Area Set 4
Finding the area of more complex polygons.
|
| | | |
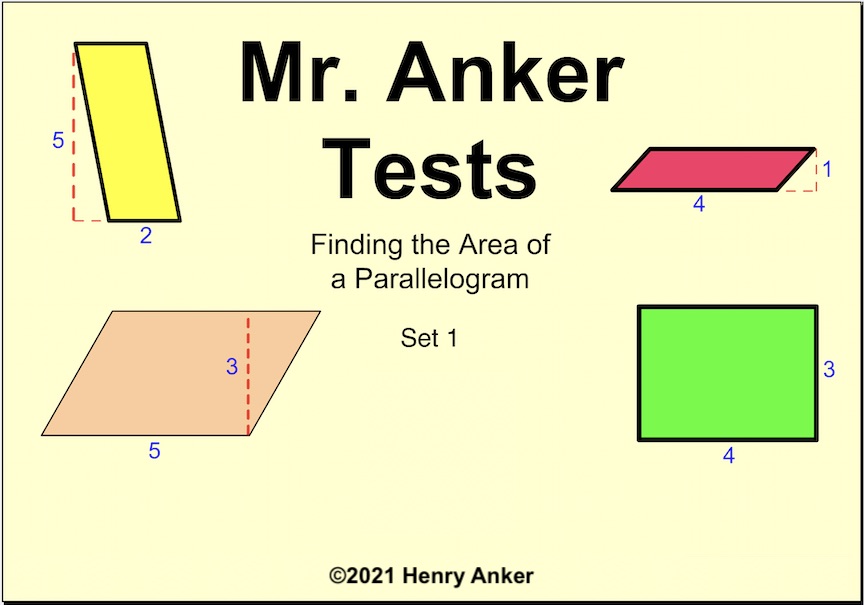
Area of Parallelograms 1
Use the formula
base x height = Area.
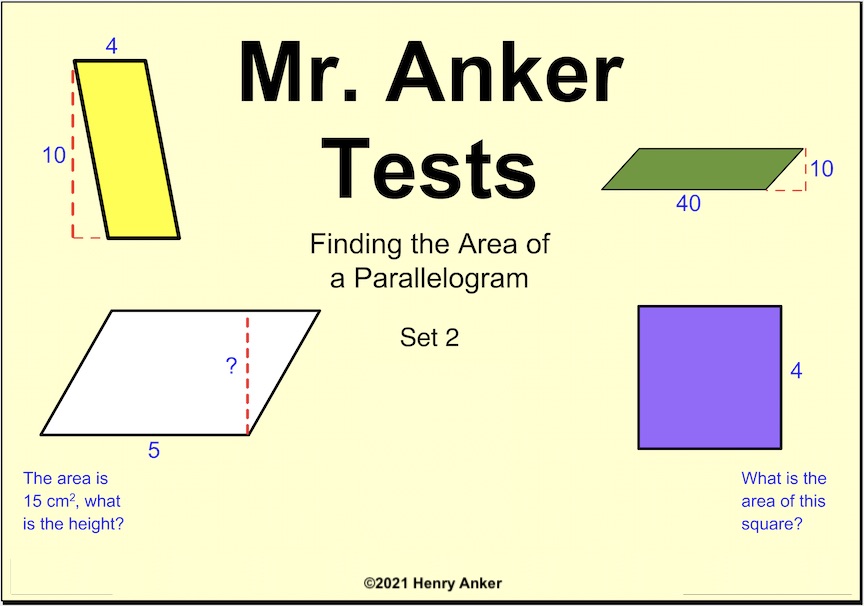
| Area of Parallelograms 2
Use the formula
base x height = Area.
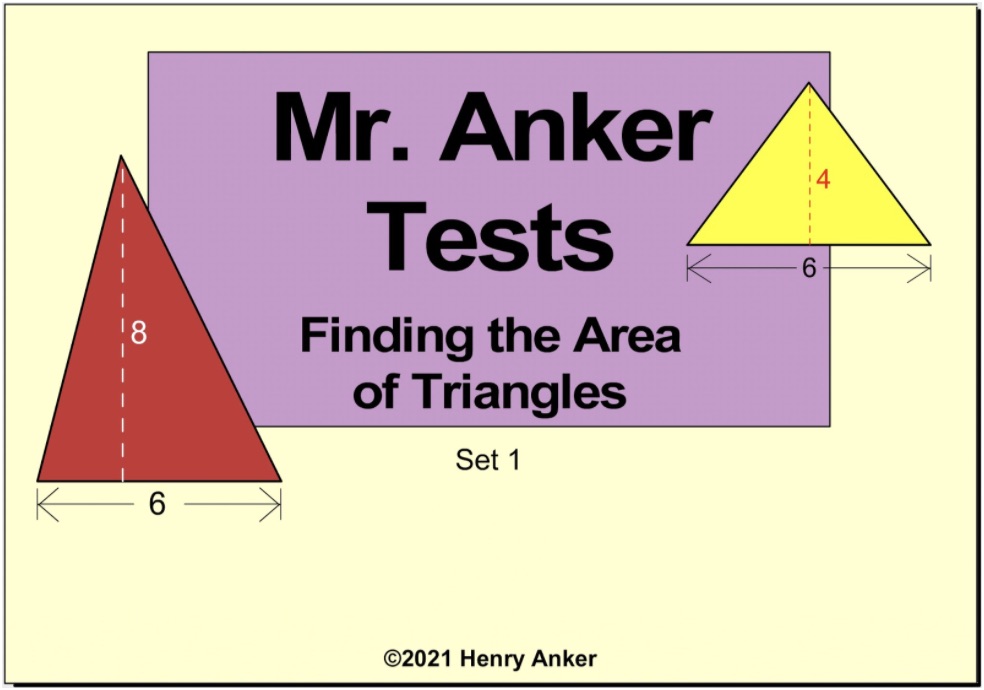
| Area of Triangles 1
Use the formula
1/2 base x height = Area.
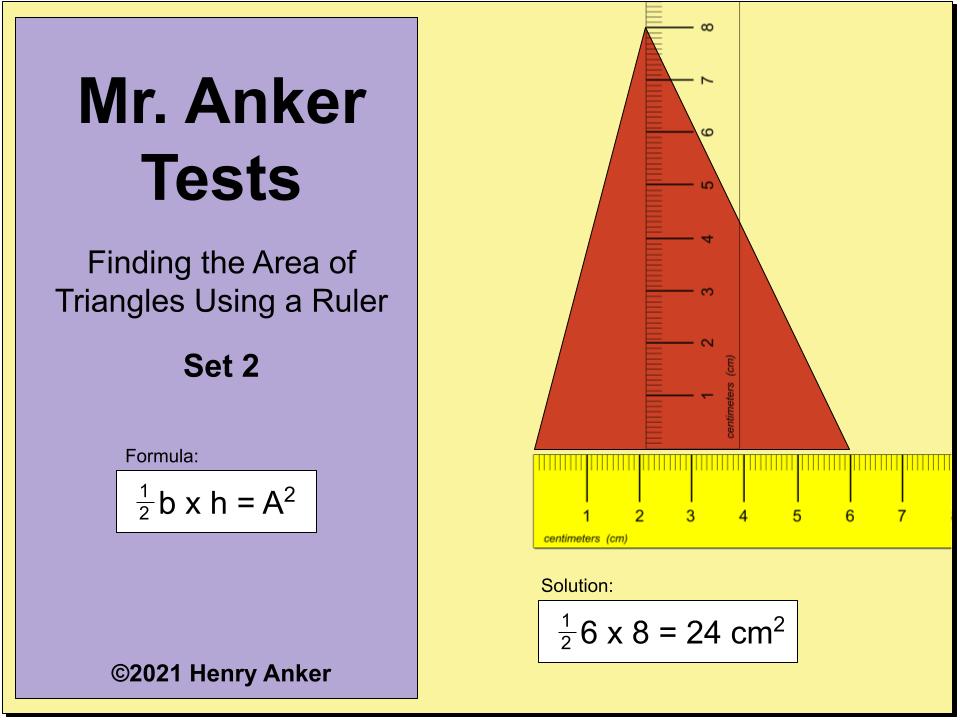
| Area of Triangles 2
Use the formula
1/2 base x height = Area.
|
| | | |
Perimeter
Perimeter 1
Calculate area of figures with integer sides.
| Perimeter 2
Calculate area, with emphasis on process and thinking algebraically.
| Perimeter 3
More challenging with an emphasis on thinking algebraically.
|
|
|
| | |
|
Perimeter & Area Using a Ruler
Finding the Perimeter Using a Ruler 1
Refer to rulers to find side lengths & add them.
| Finding the Perimeter Using a Ruler 2
Refer to rulers to find side lengths & add them.
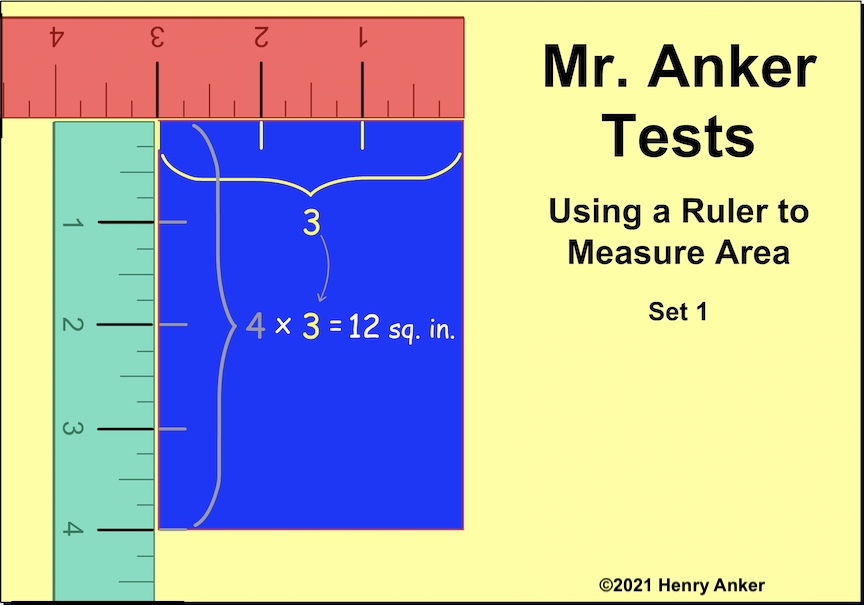
| Finding the Area Using a Ruler 1
Refer to rulers to find the area of a rectangle.
|
|
| | | |
Volume
Volume 1
Use the formula L x W x H = V(cubic units).
| Volume 2
Use the formula L x W x H = V(cubic units).
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Linear Measurement
Measurement 1
Measure to the nearest inch,
half inch, and quarter inch.
| Measurement 2
Measure to the nearest inch,
half inch, and quarter inch.
| Measurement 3
Measure to the nearest whole,
half, quarter, and eighth inch.
| Measurement 4
Measure to the nearest
sixteenth inch.
|
| | | |
Measurement 5
Measure to the nearest centimeter & exact millimeter.
| Measurement 6
Measure & compare with centimeters & millimeters.
| Measurement 7
Measure with fractions of inches, cm & mm, w/ ruler misplaced.
| Measurement 8
Enter measured values for cm, mm, & inches.
|
| | | |
Measurement 9
Measure to the nearest centimeter & exact millimeter.
| Parts of an Inch 1
Student recognizes the labeled division of an inch.
| Parts of an Inch 2
Student relies less on the labeling of an inch.
| Interactive Practice
Practice moving the ruler in this activity.
|
| | | |
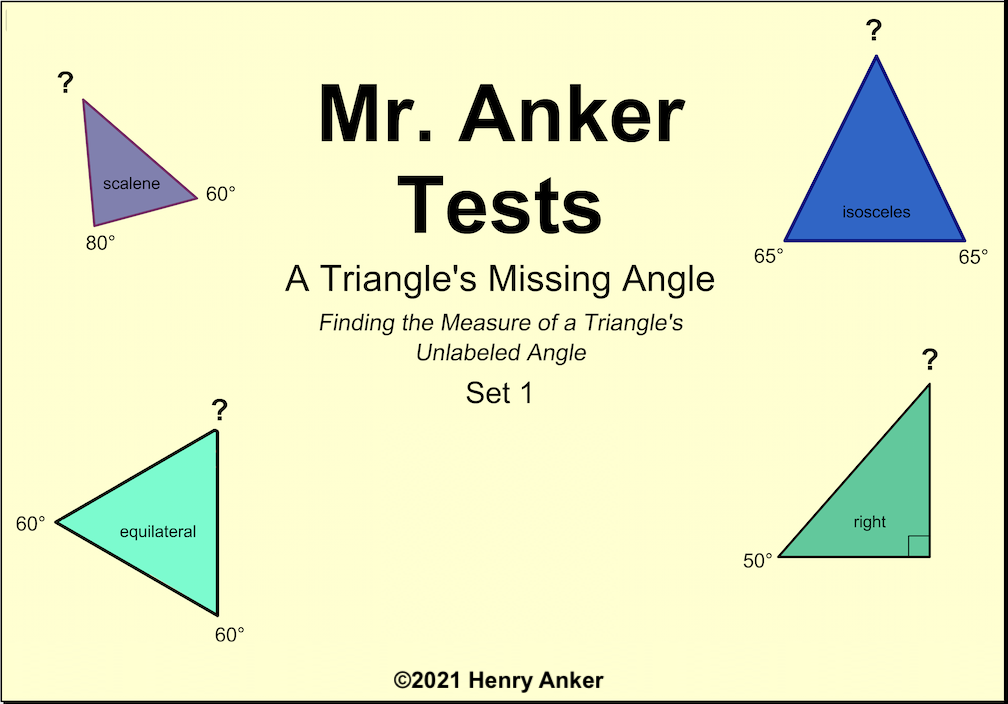
Types of Triangles
Types of Triangles 1
Determine whether a triangle is equilateral, scalene, right, isosceles, etc...
| Types of Triangles 2
Determine whether a triangle is equilateral, scalene, right, isosceles, etc...
|
|
|
|
| | |
|
Using a Protractor
Protractor 1
Find the degree measure of an angle, as well as naming some angles.
| Protractor 2
Find the degree measure of an angle, as well as naming some angles.
| Protractor 3
Find the degree measure of an angle, as well as naming some angles.
| Protractor 4
Find the degree measure of an angle, as well as naming some angles.
|
| | | |
Estimating Angles
Estimating Angles 1
Estimate the degree measure of an angle using a neighboring protractor as a reference.
| Estimating Angles 2
Estimate the degree measure of an angle using a neighboring protractor as a reference.
| Estimating Angles 3
Estimate, by entering a value, the degree measure of an angle, within 10 degrees, using a neighboring protractor as a reference.
|
|
|
| | |
Naming Angles
|